Architecture Overview
Training data shares a codebase with our parent app, DB Manager. Please look there for full documentation on back-end architecture. Within this environment, Training data uses:
/src
├── controllers
├── models
├── routes
├── services
├── middleware
├── utils
├── config
├── tests
└── app.js
Backend
Routes
API endpoints and their associated controller methods.
// routes/userRoutes.js
const express = require("express");
const userController = require("../controllers/userController");
const router = express.Router();
router.get("/users", userController.getUser);
module.exports = router;
Services
Complex business logic that isn’t directly tied to a specific endpoint.
// services/authService.js
const generateToken = (user) => {
// Logic to generate a JWT token
};
module.exports = {
generateToken,
};
Middleware
Authentication, validation and error handling.
Utils
Utility functions that can be reused across the application (p.e. formatDate).
Config
Environment variables, database configurations…
Tests
Unit and integration tests.
API
API
| Description | Endpoint | Method | Params | Body | Return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Add list of different non moodle courses | /add | POST | - | - | array of course objects: [{ "id": int, "shortname": varchar, "start_date": datetime, "language": varchar, "format": varchar, "main_topic": varchar, "level": int, "edition": int, "duration": int }, ...] |
| GET list of all non moodle courses | /getAllNMCourses | GET | - | - | array of course objects: [{ "id": int, "shortname": varchar, "start_date": datetime, "language": varchar, "format": varchar, "main_topic": varchar, "level": int, "edition": int, "duration": int }, ...] |
| GET column shortname from non_moodle_courses | /getNMCourses | GET | - | - | array of strings: ["Course1", ...] |
| Add list of different non moodle enrolments | /addEnrolment | POST | - | - | array of enrolment objects: [{ "id": int, "course_shortname": varchar, "user_fullname": varchar, "email": varchar, "country": varchar, "completion_date": datetime, "progress": int, "status": int }, ...] |
Frontend
Views
Components that hold an entire page view (containing multiple sub-components). Our only 3 views are:
├── TrainingData
├── TrainingNMCourses
├── TrainingNMEnrolments
TrainingDatais the landing page, including 2 main buttons that will redirect to either courses or enrolments.TrainingNMCoursescontains a table with all actual courses, and a button that will get a form to add more non moodle courses.TrainingNMEnrolmentsinclude button that will get a form to add more non moodle enrolments, and also a bulk user option were you can download an empty CSV and then upload all the enrolments.
User flow
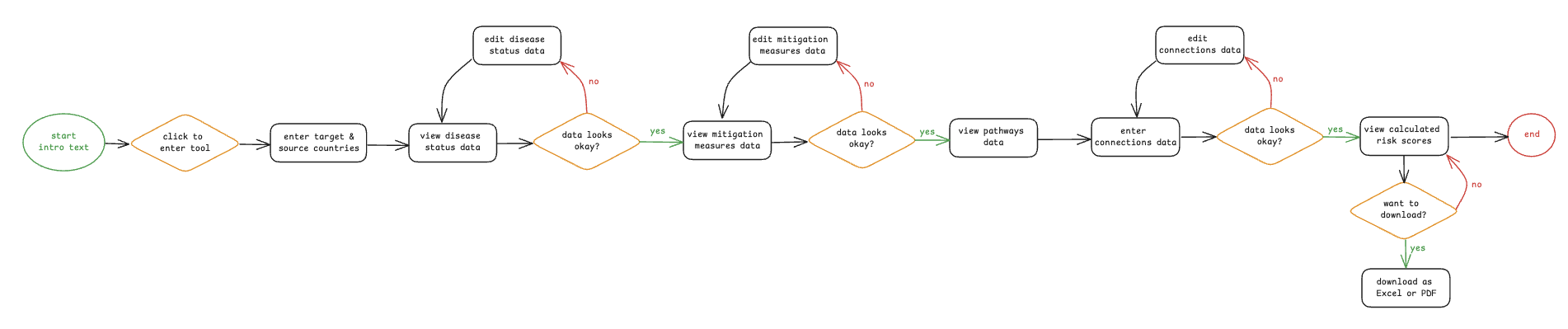
The user:
- Landing on the Training Data Main Page Interface: Displays two buttons:
[Courses]
[Enrolments]
- Navigating to Courses Action: Clicks on the [Courses] button.
Result: Redirected to the Courses page.
- Adding a Non-Moodle Course Action: Clicks [Add non-Moodle course].
Form: User fills in the required course information.
Action: Submits the form.
Result: The newly added course appears in a table with other courses listed below.
-
Returning to Main Page Action: Clicks a navigation element (e.g., Back to Training Data) to return to the main page.
-
Navigating to Enrolments Action: Clicks on the [Enrolments] button.
Result: Redirected to the Enrolments page.
- Adding a Non-Moodle Enrolment Action: Clicks [Add enrolment].
Form: User fills in the enrolment information.
Action: Submits the form.
Result: Enrolment is added to the enrolment list.
- Bulk Upload via CSV Option: User sees a section for Bulk Upload.
Step i: Clicks [Download Empty CSV] — gets a file with required columns.
Step ii: Fills out the CSV with enrolment data.
Step iii: Clicks [Upload CSV] — submits the populated file.
Style guide
Follow EUFMD's Engineering Guidelines. In addition to those, we do the following:
Vue API
- Use Vue Options API
- There is also the new Composition API, but the original dev team was more familiar with Options format.
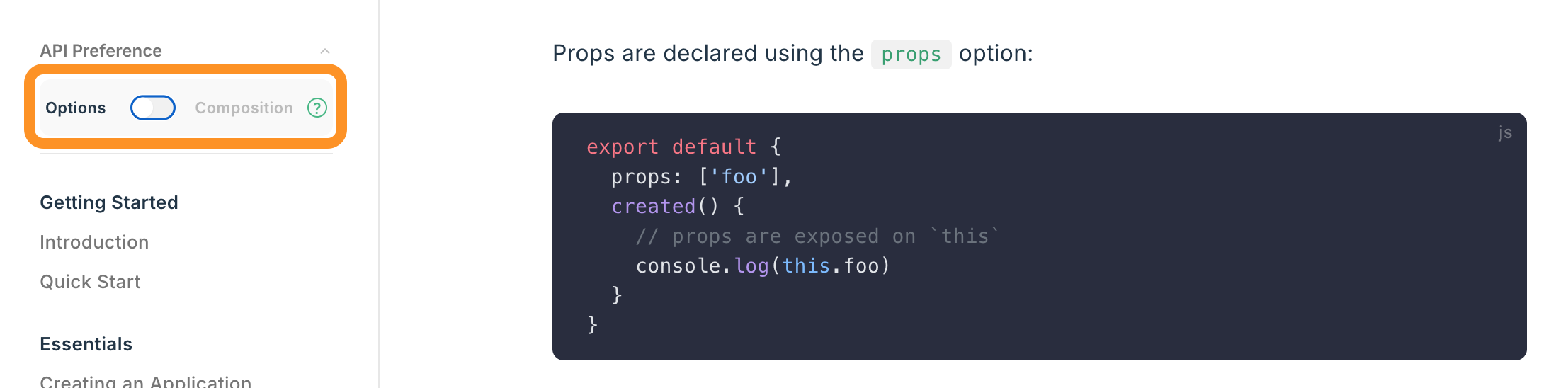
- If looking up documentation, make sure the “Options” format is selected:
Naming conventions
- custom events (
$emits) inkebab-case - data/variable names in
camelCase - component names should be:
- in
PascalCase - always multi-word: i.e.
- ❌
Connections.vue - ✅
ConnectionsTable.vue
- ❌
- when components are used by only one parent: prepend with their parent name, i.e. if a Form has components Question and Answers:
- ❌
Question.vueAnswers.vue - ✅
FormQuestion.vue,FormAnswers.vue - This ensures that related components are visually grouped together in the file structure.
- ❌
- when components are reused throughout the app: prepend with
RMT. For example, if we reuse the sameButton:- ❌
Button.vue - ✅
RMTButton.vue - This ensures that reusable components are visually grouped together in the file structure
- ❌
- in
Pinia for state management
Read and follow tutorial here, and examples in client > src > stores.