Data flow in a React application
Understanding Data Flow in a React Application with MySQL and an API
Introduction
Building modern web applications often involves fetching data from a backend server and displaying it on the frontend. In this post, we'll explore how data flows from a MySQL database to a React frontend through an API layer. Whether you're new to data flow or looking to reinforce your understanding, this guide will break down each step in a simple and clear manner.
What We'll Cover
- MySQL Database
- API Layer
- React Frontend
- Putting It All Together
MySQL Database
MySQL is a popular relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores data in tables. Each table has rows and columns, where rows represent individual records and columns represent the attributes of those records.
Example: stories Table
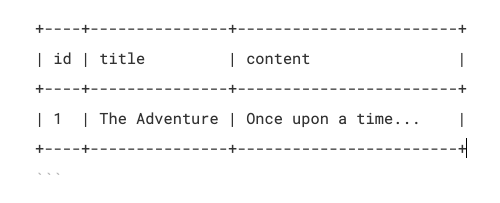
In this table, we have three columns: id, title, and content. Each row represents a story.
API Layer
The API (Application Programming Interface) acts as an intermediary between the frontend and the database. It defines a set of endpoints that the frontend can call to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
Example API Endpoint
GET /api/stories/:id: Fetches a story by its ID.
Node.js/Express API Code
const express = require('express');
const mysql = require('mysql');
const app = express();
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: 'password',
database: 'stories_db'
});
app.get('/api/stories/:id', (req, res) => {
const storyId = req.params.id;
const query = 'SELECT * FROM stories WHERE id = ?';
connection.query(query, [storyId], (error, results) => {
if (error) {
return res.status(500).json({ error: 'Database error' });
}
if (results.length > 0) {
res.json(results[0]);
} else {
res.status(404).json({ error: 'Story not found' });
}
});
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
React Frontend
React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. React components manage their own state and can fetch data from APIs to update the UI dynamically.
React Component Code
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Story() {
const [story, setStory] = useState(null);
const fetchStory = async (id) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`/api/stories/${id}`);
const data = await response.json();
setStory(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching story:', error);
}
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => fetchStory(1)}>Fetch Story</button>
{story && (
<div>
<h1>{story.title}</h1>
<p>{story.content}</p>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default Story;
Putting It All Together
Let's walk through the complete process of fetching and displaying data in a React application.
Step 1: User Action (React Component)
A user clicks a button in the React component to fetch a story.
Step 2: API Request (Frontend to API)
The React component makes an HTTP GET request to the API endpoint to fetch the story data.
const fetchStory = async (id) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`/api/stories/${id}`);
const data = await response.json();
setStory(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching story:', error);
}
};
Step 3: Database Query (API)
The API receives the request, processes it, and sends a SQL query to the MySQL database to retrieve the story data
SELECT * FROM stories WHERE id = 1;
Step 4: Data Retrieval (Database to API)
The MySQL database executes the SQL query, retrieves the data, and sends it back to the API.
Step 5: Response to Frontend (API to Frontend)
The API formats the retrieved data as JSON and sends it back to the React component.
{
"id": 1,
"title": "The Adventure",
"content": "Once upon a time..."
}
Step 6: Rendering (React Component)
The React component receives the data and updates its state, which triggers a re-render to display the story.
{story && (
<div>
<h1>{story.title}</h1>
<p>{story.content}</p>
</div>
)}
Conclusion
By understanding how data flows from a MySQL database to a React frontend through an API layer, you can build more dynamic and responsive web applications. This process ensures that users can interact with data seamlessly, making for a better user experience.
Happy coding!
